 juin 5, 2024
juin 5, 2024
How to Choose between API and EDI Connectivity?
For a long time, the logistics industry was trapped in the age of email, fax, and paper for managing their communications, and while many are still stuck in the past, others are embracing the evolution of technologies with APIs and EDI. These systems allow for the seamless transfer of data, real-time visibility, heightened accuracy, and more. With supply chains being relied on to keep your business running, creating and maintaining an efficient line of communication with all parties is crucial for success.
What are APIs?
- An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate and interact with each other. It defines the methods and data formats that applications can use to request and exchange information, enabling seamless integration and functionality across various platforms and systems.
- For more information about the functions and nitty-gritty of APIs check out this MuleSoft article.
How are APIs used in logistics?
APIs are used for a wide range of purposes in logistics including:
- Real-time shipment tracking
- Inventory management
- Order processing
- Payment and Financial Transactions
APIs enable seamless integration between different systems and platforms used by 3PL providers, and customers.
What are the benefits of using APIs in logistics?
- Real-time data: Logistics APIs enable real-time data exchange, allowing faster and more dynamic communication between systems.
- Flexibility: Logistics APIs offer more flexibility regarding data exchange formats and can support various data types, including JSON and XML.
- Automation: Logistics APIs enable automated order processing, enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What are the challenges of using APIs?
- Standardization: APIs may lack standardized formats, requiring more effort in API design, documentation, and implementation.
- Security: API security measures need to be robust to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
What is EDI?
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a system for the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standardized format. It enables seamless communication and transaction processing, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, without the need for human intervention.
- EDI streamlines business processes, reduces errors, and enhances efficiency by automating data exchange, cutting down on paper usage, and eliminating manual data entry. It utilizes structured data formats to ensure compatibility and consistency for all partners.
For more information about the technicalities and integration of EDI check out this Amazon Web Services article.
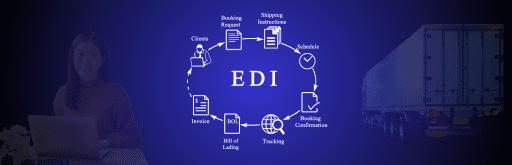
Is EDI outdated?
EDI has been a cornerstone of B2B communication for decades and is still commonly used today, enabling smooth operations in various industries worldwide.
How are EDIs used in logistics?
In Trucking logistics, EDI is commonly used for exchanging standardized documents and information between 3PL providers, Carriers and Shippers such as:
- Load tenders
- Status updates
- Location updates
- Invoices
Common EDI Transaction Codes in Over the Road Trucking logistics:
EDI 204 – Motor Carrier Load Tender: This is an EDI document used by shippers to offer a truckload or less than truckload (LTL) shipment to a carrier.
EDI 210 – Motor Carrier Freight Details and Invoice: This is an electronic invoice that is usually sent from the carrier to a shipper to request payment for freight charges.
EDI 214 – Transportation Carrier Shipment Status Message: This is usually sent by a transportation carrier such as a trucking or third-party logistics company (3PL) to a shipper or buyer to allow them to track their shipments and receive status updates.
EDI 990 – Response to a Load Tender: This is a response to the EDI 204 transaction where the motor carrier can either accept or reject the shipment offer.
To learn about more EDI transaction types check out this TrueCommerce article.
What are the benefits of using EDIs in logistics?
- Standardization: EDI relies on standardized formats for data exchange, ensuring compatibility across different systems and partners.
- Stability: It has been a longstanding technology in logistics, with many established protocols and implementations.
- Batch Processing: EDI is particularly efficient for batch processing of large volumes of transactions.
What are the challenges of using EDIs?
- Lack of Real-Time Data: EDI transactions are typically asynchronous, therefore the system is only updated at certain times and cannot provide live data.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing EDI systems can be complex and costly, especially for smaller businesses.
Is API or EDI Better?
The debate over API vs EDI is based on two false premises; first, that there is a one-size fits all solution and two, that there has to be one over the other. Every company is different and whether API or EDI will better suit their needs depends on their individual situation. Additionally, EDI and API don’t have to be used separately at all, so there is no need to make a competition out of tools that can and are currently being used in tandem.
How to know whether API or EDI is best for you?
Navigating the benefits and drawbacks of APIs and EDIs can be difficult but here at Première frontière logistique we can support you on whichever solution you wish to utilize.
- EDI Integration: First Frontier utilizes EDI for exchanging standardized documents such as shipment tenders, tracking updates, delivery confirmations, and invoices with clients. This would ensure smooth communication and transaction processing, especially for batch operations and legacy systems.
- API Connectivity: First Frontier also provides API connections for our clients, so reach out to learn more about how API can connect our business to yours.






