 juillet 26, 2024
juillet 26, 2024
Full Truck Load Shipping: Benefits, Costs, and Best Practices
Full Truck Load (FTL) shipping is a cornerstone of the logistics and transportation industry, particularly for businesses requiring efficient, large-scale transportation of goods. This comprehensive guide will delve into every aspect of FTL shipping, helping you understand its importance, when to use it, and how it differs from other shipping methods like Less Than Truck Load (LTL) and Partial Truck Load (PTL).
What is Full Truck Load (FTL) Shipping?
Chargement complet du camion(FTL) shipping refers to the use of an entire truck’s capacity to transport goods from one location to another. Unlike Moins que la charge du camion (LTL), where shipments from multiple customers share space in a single truck, FTL dedicates the entire truck to a single shipment. This method is particularly beneficial for companies that need to move large volumes of goods efficiently and securely.
Advantages of Full Truck Load (FTL) Shipping
1. Faster Transit Times
Since the truck is dedicated to one shipment, there are no additional stops along the route. This results in quicker delivery times compared to LTL shipping, where multiple pickups and drop-offs can cause delays.
2. Reduced Risk of Damage
With FTL shipping, the goods are loaded once and remain untouched until they reach their destination. This minimizes the risk of damage that can occur with frequent handling in LTL shipments.
3. Cost-Effective for Large Shipments
For companies with large quantities of goods, FTL can be more economical. The cost per unit decreases as the shipment size increases, making it a cost-effective option for bulk transportation.
4. Increased Security
The fewer touch points in FTL shipping enhance security, reducing the risk of theft or loss. The load remains untouched until it reaches its final destination, ensuring that the shipment is secure throughout the journey.

When to Use FTL vs. LTL?
Deciding between Chargement complet du camion(FTL) and Moins que la charge du camion (LTL) shipping depends on several factors:
Shipment Size and Weight
- FTL: Ideal for large shipments that can fill an entire truck.
- LTL: Suitable for smaller shipments that do not require the full capacity of a truck.
Delivery Speed
- FTL: Faster delivery due to direct routes with no additional stops.
- LTL: Slower due to multiple stops for pickups and deliveries. Additionally, LTL shipments often go through cross-docking facilities and work through a network of distribution centers, which can add to transit time but help in optimizing routes and consolidating freight.
Budget Considerations
- FTL: More cost-effective for large shipments as the cost is spread over a larger number of units.
- LTL: Generally cheaper for smaller shipments, as costs are shared with other shippers.
Risk of Damage
- FTL: Lower risk due to minimal handling.
- LTL: Higher risk with more frequent handling and transfers.
What is the Difference Between PTL and FTL?
Partial Truck Load (PTL)
- PTL: Also known as Partial Truckload or Volume LTL, PTL falls between LTL and FTL. It is used for shipments that are too large for LTL but do not require the full capacity of a truck.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than LTL but cheaper than FTL.
- Handling and Timing: Fewer touch points compared to LTL, reducing the risk of damage. However, PTL shipments share truck space, so any delay with one shipment can impact the entire load, leading to potential timing issues and reduced control over delivery schedules.
Chargement complet du camion(FTL)
- FTL: Utilizes the entire truck for a single shipment.
- Cost: More economical for large shipments as the cost per unit decreases with volume.
- Handling: Minimal handling, reducing the risk of damage and increasing security. Also offers better timing and control, as the shipment follows a direct route without stops, leading to faster and more predictable delivery times.
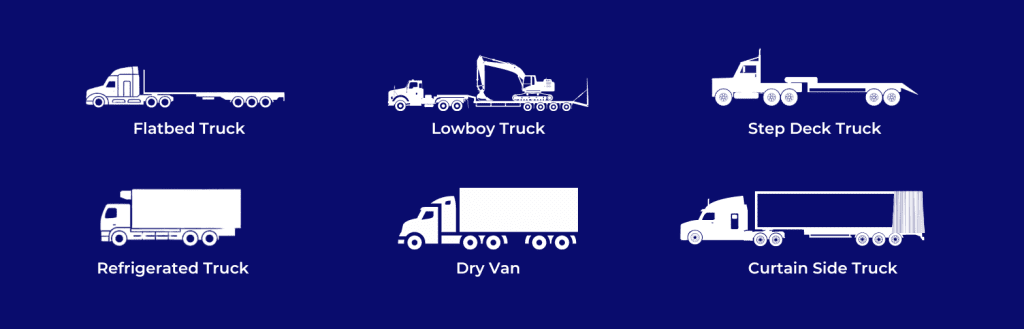
Types of Equipment Used for Full Truck Load (FTL) Shipments
Selecting the right equipment for Full Truck Load (FTL) shipments is crucial for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness of transporting goods. Various types of trucks and trailers are available, each designed to meet specific transportation needs. Here is an overview of the different types of equipment commonly used for FTL shipments.
1. Dry Vans
Dry vans are the most common type of trailer used for FTL shipments. They are enclosed trailers that protect cargo from external elements like weather and road debris.
Applications
- General freight: Suitable for a wide range of goods, including non-perishable food items, clothing, electronics, automotive parts and household goods.
- Secure transport: The enclosed design ensures security and reduces the risk of theft or damage.
2. Flatbed Trailers
Flatbed trailers have an open, flat deck without sides or a roof. This design allows for easy loading and unloading of goods from all sides.
Applications
- Oversized cargo: Ideal for transporting large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped items such as machinery, construction materials, and large equipment.
- Versatility: Can carry loads that exceed the dimensions of a dry van, including wide and tall items.
3. Refrigerated Trailers (Reefers)
Refrigerated trailers, or reefers, are equipped with temperature control systems to keep perishable goods at a specific temperature during transit.
Applications
- Perishable goods: Essential for transporting food, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive items.
- Fresh produce: Ensures fruits and vegetables remain fresh from farm to market.
4. Step Deck Trailers
Step deck trailers, also known as drop decks, have a lower deck height than standard flatbeds, allowing for taller cargo without exceeding height restrictions.
Applications
- Tall equipment: Suitable for transporting items that are too tall for a standard flatbed, such as construction machinery and large equipment.
- Easy loading: The lower deck height makes loading and unloading easier.
5. Lowboy Trailers
Lowboy trailers have an even lower deck than step decks, designed specifically for hauling extremely heavy and tall loads.
Applications
- Heavy equipment: Used for transporting construction and industrial machinery that exceed standard height and weight limits.
- Specialized transport: Ideal for oversized loads that require a lower center of gravity for stability.
6. Curtain Side Trailers
Curtain side trailers have retractable curtains on the sides that can be pulled back to allow side loading and unloading.
Applications
- Ease of access: Ideal for freight requiring side loading or unloading, providing easier access compared to dry vans.
- Versatile cargo: Suitable for a various goods that need protection from the elements but require quick loading/unloading.

How Much Does It Cost to Ship a Full Truckload?
Shipping a full truckload (FTL) is influenced by several factors that can cause costs to fluctuate. Understanding these factors can help businesses budget more accurately and optimize their shipping strategies. Here is an overview of the typical costs associated with FTL shipping and the key factors that influence these rates.
Average Cost of FTL Shipping
The cost of shipping a full truckload can vary widely and for specialized equipment like refrigerated trailers or flatbeds, rates can be higher. However, rates can fluctuate based on several influencing factors.
Factors Affecting FTL Shipping Rates
1. Time of Year and Season
The time of year can significantly impact FTL shipping rates. During peak seasons, such as the holiday period in late fall and early winter, rates often increase due to higher demand for shipping services. Similarly, specific industries have their peak seasons, which can also drive up costs. For example:
- Retail: Higher rates during the holiday shopping season.
- Agriculture: Increased demand during harvest seasons.
2. Type of Freight
The nature of the freight being transported can affect the cost:
- Standard Dry Van Freight: Generally the least expensive option.
- Refrigerated Freight (Reefers): Higher costs due to temperature control requirements.
- Hazardous Materials: Additional handling and safety regulations can increase rate. HAZMAT requires certified drivers who are trained in handling and safely transporting such cargo.
- Oversized or Heavy Loads: Specialized equipment like flatbeds or lowboy trailers will cost more. This type of freight also requires more time and experienced drivers with specialized skills, further increasing the overall cost. The equipment itself is more expensive, and the handling of such loads demands more precision and expertise.
3. Location and Distance
Geographical factors play a crucial role in determining shipping costs:
- Distance: Longer distances generally result in higher costs, though the rate per mile may decrease.
- Origin and Destination: Shipping rates can vary based on the location of pickup and delivery. Remote or less accessible areas may incur higher charges due to limited availability of carriers. Additionally, the amount of available freight in that area and the availability of backhauls can also impact rates. Areas with low freight volume or limited opportunities for return loads may see higher costs due to decreased carrier efficiency.
4. Fuel Prices
Fluctuating fuel prices have a direct impact on shipping costs. Carriers often include a fuel surcharge to account for changes in diesel prices. When fuel prices rise, the overall cost of FTL shipping will also increase.
5. Demand and Capacity
Market demand and available capacity are significant factors:
- High Demand: When demand for trucks exceeds supply, rates increase. This is common during peak shipping seasons or periods of economic growth.
- Low Demand: Rates may decrease when there is an oversupply of trucks or during off-peak times.
6. Additional Services
Additional services required for the shipment can also affect costs:
- Expedited Shipping: Faster delivery times come with higher rates. This may involve using teams of two drivers to keep the load moving continuously without rest stops, ensuring the quickest possible delivery.
- Accessorial Charges: Fees for services like liftgate, residential delivery, or inside delivery can add to the total cost.
- Insurance: Adding insurance to protect against potential damages or losses will increase costs. For high-value freight, the risk if damaged or stolen may be a significant factor, necessitating higher insurance coverage and further increasing expenses.

How FTL Transport Works
Understanding the process of FTL transport can help businesses optimize their logistics and ensure efficient transportation of goods.
1. Booking the Shipment
The first step involves booking the FTL service with a transportation provider. This includes providing details about the shipment, such as weight, volume, pickup and delivery locations, and any special requirements.
2. Loading the Truck
Once booked, the transportation provider arranges for a truck to be loaded with the shipment. In FTL shipping, the shipper is responsible for loading the truck. Proper loading techniques are essential to ensure the safety and security of the goods during transit. This involves carefully placing and securing of items to prevent shifting and damage during the journey.
3. Transportation
The truck follows a direct route from the pickup location to the delivery destination. Since the truck is dedicated to one shipment, there are no additional stops, resulting in faster transit times. Real-time tracking can be utilized to monitor the progress of the shipment and ensure timely delivery.
4. Unloading
Upon reaching the destination, the goods are unloaded and delivered to the recipient. The Bill of Lading (BOL) plays a crucial role in this process. It is a legal document that details the type, quantity, and destination of the goods being carried. It serves as a receipt of freight services and a contract between the shipper and carrier.
When unloading, it is imperative to inspect the goods and mark down any damages seen on delivery. Noting damages on the BOL is essential for filing claims and ensuring accountability. This step helps protect against potential disputes and ensures that any issues are promptly addressed.
Key Considerations for Choosing FTL Services
When selecting FTL services, businesses should consider several factors to ensure they choose the right provider and optimize their shipping process.
1. Reliability and Reputation
Choose a transportation provider with a proven track record of reliability and customer satisfaction. Look for reviews, testimonials, and references to gauge their performance.
2. Coverage and Network
Ensure the provider has a comprehensive network and coverage in the regions where you need to ship goods. This ensures smooth and efficient transportation.
3. Equipment and Fleet
Check the provider’s fleet and equipment to ensure they can handle your specific shipment requirements. Modern, well-maintained trucks are essential for reliable and safe transportation.
4. Pricing and Contracts
Compare pricing and contract terms from multiple providers to get the best deal. Be clear about the costs involved and any additional fees that may apply.
5. Customer Support
Good customer support is crucial for addressing any issues or concerns that may arise during the shipping process. Choose a provider with responsive and helpful customer service.

FTL Shipping in Canada
In Canada, FTL shipping plays a vital role in the transportation of goods across vast distances. The country’s large landmass and diverse geography make FTL an essential service for businesses that need to move large volumes of goods efficiently.
Benefits of FTL Shipping in Canada
- Efficient Long-Distance Transportation: FTL is ideal for moving goods over long distances, such as coast-to-coast shipments.
- Cross-Border Shipping: FTL services can facilitate cross-border shipments between Canada and the United States, ensuring seamless transportation of goods.
- Industry Support: Canada’s robust logistics and transportation industry supports various sectors, including manufacturing, retail, and agriculture, with reliable FTL services.
Cross-Border FTL Shipping: Canada, USA, and Mexico
Cross-border FTL shipping between Canada, the USA, and Mexico is a critical component of the North American supply chain. This segment will explore the intricacies and benefits of cross-border FTL transport.
Benefits of Cross-Border FTL Shipping
1. Seamless Integration
FTL services facilitate seamless integration between the three countries’ supply chains, enabling efficient movement of goods across borders. This is particularly important for industries like automotive, manufacturing, and agriculture that rely on components and materials from multiple countries.
2. Reduced Transit Times
Cross-border FTL shipping reduces transit times by minimizing stops and ensuring direct routes. This is especially beneficial for time-sensitive shipments that need to reach their destination quickly.
3. Consistency and Reliability
FTL providers specializing in cross-border transport often have established routes and partnerships, ensuring consistent and reliable service. This reduces the risk of delays and disruptions in the supply chain.
4. Simplified Customs Process
Experienced FTL providers understand the complexities of customs regulations in each country and can facilitate smoother customs clearance. This includes accurate documentation and compliance with regulatory requirements.

Key Considerations for Cross-Border FTL Shipping
1. Regulatory Compliance
Ensure compliance with the regulatory requirements of each country. This includes understanding tariffs, duties, and import/export regulations to avoid delays and penalties.
2. Proper Documentation
Accurate and complete documentation is essential for cross-border shipments. This includes commercial invoices, bills of lading, and any required permits or certificates.
3. Carrier Selection
Choose a carrier with experience in cross-border FTL shipping. Look for providers with a strong network, expertise in customs procedures, and a proven track record of successful cross-border deliveries.
4. Insurance
Consider obtaining insurance for cross-border shipments to protect against potential risks such as theft, damage, or loss. This provides peace of mind and financial protection in case of unforeseen events.
5.Customs Broker
Utilizing a customs broker can simplify the process of cross-border shipping. A customs broker is an expert in customs regulations and can assist with:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring all shipments meet the import/export regulations of each country.
- Documentation: Handling and submitting the necessary paperwork accurately and efficiently to avoid delays.
- Duties and Tariffs: Calculating and advising on the correct tariffs and duties applicable to the shipment.
- Problem Resolution: Addressing and resolving any issues that arise during the customs clearance process, helping to prevent delays and additional costs.
Popular Cross-Border Routes
- Canada-USA: Major routes include the Windsor-Detroit corridor, the Niagara Peninsula, and the Pacific Northwest. These routes facilitate significant trade volumes between the two countries.
- USA-Mexico: Key routes include Laredo, Texas, which is a major crossing point for goods moving between the USA and Mexico, particularly for the automotive and manufacturing industries.
- Canada-Mexico: Although less common, there are established routes for direct shipments between Canada and Mexico, often involving transshipment through the USA.
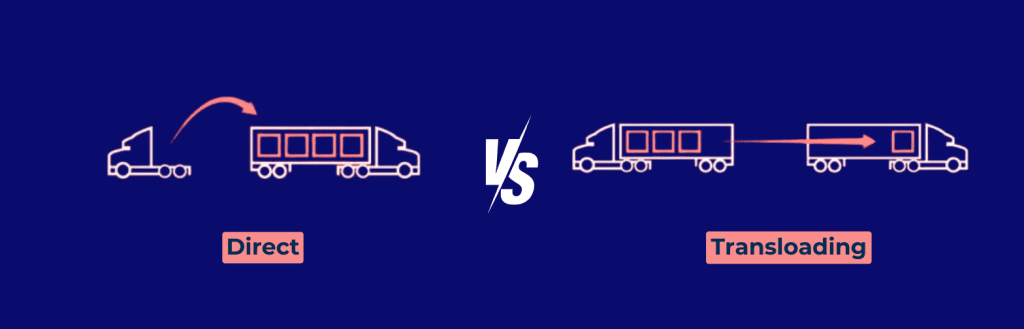
Direct Door-to-Door vs. Transloading
Direct Door-to-Door
The Door to Door option provides a seamless shipping experience from the point of origin to the final destination without changing carriers or handling the cargo. It offers:
- Speed: Faster transit times with fewer stops.
- Security: Less handling reduces the risk of damage or theft.
- Simplicity: Simplified logistics and documentation processes.
Transloading
Transloading involves transferring cargo from one mode of transport to another or from one truck to another at a designated point, often near borders. It offers:
- Flexibility: Adaptability for shipments with varying logistics needs.
- Cost Efficiency: Potentially lower costs by optimizing the use of different transport modes.
- Complexity Management: Effective for managing complex supply chains with multiple stops or destinations.
By understanding these options, businesses can choose the most suitable method for their cross-border FTL shipments, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Tips for Optimizing FTL Shipping
Optimizing Full Truck Load (FTL) shipping can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure the timely delivery of goods. Here are some key tips to help you achieve optimal results:
1. Proper Packaging
Ensure that goods are properly packaged to withstand the rigors of transportation. Use appropriate materials and techniques to secure the shipment. Proper packaging prevents damage during transit and can help streamline the loading and unloading process.
2. Accurate Documentation
Provide accurate and complete documentation to avoid delays and issues during transit. This includes shipping labels, invoices, bills of lading, and any required permits or certificates. Clear and precise documentation is essential for smooth customs clearance and regulatory compliance.
3. Plan Ahead
Plan shipments well in advance to secure availability and avoid last-minute rushes. Early planning can help optimize routes, reduce costs, and ensure that you can meet your delivery timelines. Proactive scheduling allows for better coordination with carriers and other logistics partners.
4. Utilize Technology
Leverage technology to track shipments and monitor their progress in real-time. This helps in managing the supply chain more effectively and addressing any issues promptly. Implementing technologies like Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Application Programming Interface (API) connections can enhance data accuracy and streamline communication between shippers and carriers.
- EDI: Automates the exchange of shipping documents and other information, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
- API: Enables real-time data sharing and integration with various logistics platforms, providing up-to-date information on shipment status and helping with better decision-making.
5. Collaborate with Providers
Work closely with your transportation provider to ensure clear communication and smooth coordination. Establishing a strong partnership can lead to better service and reliability. Regularly review performance, address any issues promptly, and collaborate on strategies to improve the efficiency of the shipping process.
Conclusion
Full Truck Load (FTL) shipping is an essential service for businesses that need to transport large volumes of goods efficiently and securely. Understanding when to use FTL vs. LTL, the benefits of FTL transport, and key considerations for choosing FTL services can help businesses optimize their logistics and ensure successful shipments.
Whether you are shipping within Canada or across borders, First Frontier Logistics offers FTL shipping services to suit your needs. Contact us to enhance your North American supply chain with our experience in providing the seamless, efficient, and reliable transport of goods across borders.






